
5 Best Reading Assistance Tools for Dyslexia in 2025
Table of Contents
- What Are the Main Reading Challenges Dyslexia Creates for?
- How Does Assistive Technology Benefit Dyslexic Readers?
- Reading Assistance Tools for Dyslexia: Which Options Provide the Best Reading Support?
- Speaktor
- ReadSpeaker
- Voice Dream Reader
- Microsoft Immersive Reader
- Speechify
- How Does Text-to-Speech Technology Work for Dyslexia?
- How to use Speaktor for Reading Assistance for Dyslexia?
- Conclusion
Transcribe, Translate & Summarize in Seconds
Table of Contents
- What Are the Main Reading Challenges Dyslexia Creates for?
- How Does Assistive Technology Benefit Dyslexic Readers?
- Reading Assistance Tools for Dyslexia: Which Options Provide the Best Reading Support?
- Speaktor
- ReadSpeaker
- Voice Dream Reader
- Microsoft Immersive Reader
- Speechify
- How Does Text-to-Speech Technology Work for Dyslexia?
- How to use Speaktor for Reading Assistance for Dyslexia?
- Conclusion
Transcribe, Translate & Summarize in Seconds
Reading assistance dyslexia tools transform difficult text into accessible content for individuals with reading challenges. Approximately 10% of the population exhibits dyslexia symptoms, making effective reading assistance technology essential for academic success, professional development, and daily information processing. Reading assistance dyslexia solutions incorporate text-to-speech capabilities and customizable interfaces to overcome neurological reading barriers.
The most effective reading assistance dyslexia tools in 2025 include:
- Speaktor: Premium text-to-speech solution with natural-sounding voices across 50+ languages
- ReadSpeaker: A platform with exceptional institutional integration for organizations
- Voice Dream Reader: Mobile-optimized reading experience ideal for students on the go
- Microsoft Immersive Reader: Seamless integration with Office applications for workplace use
- Speechify: User-friendly interface with minimal setup, perfect for non-technical users

What Are the Main Reading Challenges Dyslexia Creates for?
Dyslexia creates specific neurological reading obstacles that impact how written information is processed. People experiencing dyslexia frequently encounter difficulties with phonological processing, working memory capacity, and rapid visual-verbal responding abilities. These challenges manifest through symptoms including reduced reading speed, poor spelling accuracy, difficulty recognizing previously learned words, and comprehensive reading comprehension challenges.
Reading assistance dyslexia technology addresses these specific neurological patterns. The reading difficulties associated with dyslexia are not related to general intelligence levels—many individuals with dyslexia demonstrate above-average creativity and problem-solving capabilities. The fundamental challenge involves accessing written information efficiently through traditional reading methods.
How Does Assistive Technology Benefit Dyslexic Readers?
Assistive technology for reading difficulties provides transformative advantages for individuals with dyslexia. Reading assistance dyslexia tools improve reading speed and comprehension while simultaneously reducing cognitive fatigue typically associated with text decoding. This specialized technology enhances independence in academic environments and professional settings, creating significant confidence improvements and self-efficacy development.
By delivering multiple sensory inputs, such as visual tracking combined with auditory information, users can adjust the text to speech speed listen to their preference, making modern dyslexia-friendly reading technology work with the brain's natural strengths rather than against its inherent challenges. Audio reading assistance creates accessible pathways to academic achievement and professional success that were previously difficult to navigate for dyslexic individuals.
Reading Assistance Tools for Dyslexia: Which Options Provide the Best Reading Support?
Reading assistance dyslexia technology transforms how individuals with reading challenges interact with text. Selecting the right dyslexia reading software significantly impacts academic performance, workplace productivity, and overall quality of life for those with reading difficulties.
Assistive technology for reading difficulties must balance natural voice quality, format compatibility, customization options, and cost-effectiveness to provide truly transformative reading experiences.
Each reading assistance dyslexia solution offers distinct advantages for different user needs and environments. The following detailed reviews examine specific features and benefits of each tool for supporting individuals with dyslexia.
Speaktor
Speaktor is a premium text-to-speech solution specifically designed for individuals with dyslexia. It focuses on delivering remarkably natural-sounding speech to minimize listening fatigue while supporting multiple document formats and languages. With cloud-based functionality and customizable settings, it aims to be a comprehensive reading assistance tool for academic and professional settings.
Pros:
- Extensive language support with 50+ languages and 15+ natural-sounding voice options
- Wide format compatibility (PDF, DOCX, TXT)
- Highly customizable (reading speed, voice type, pronunciation)
- Synchronized text highlighting for visual-auditory reinforcement
- Cloud-based storage enabling cross-device access
- Premium voice quality that closely resembles human speech
Cons:
- Likely comes with premium pricing (based on "premium" positioning)
- May require more system resources due to high-quality voice synthesis
- Potentially steeper learning curve due to extensive customization options
- Cloud-based approach may require internet connectivity for full functionality
- It might be overkill for users with basic reading assistance needs
ReadSpeaker
ReadSpeaker is an enterprise-focused solution designed for institutional implementation and accessibility compliance. It emphasizes seamless integration with learning management systems and organizational infrastructure to provide consistent reading experiences across educational and corporate environments.
Pros:
- Strong institutional integration capabilities for large-scale deployment
- Browser extension for direct webpage reading without format conversion
- Compatible with major learning management systems
- Consistent voice quality across platforms
- Designed to meet organizational accessibility compliance requirements
- Approximately 25 language options
Cons:
- Primarily designed for institutional use rather than individual consumers
- Likely requires enterprise-level pricing and licensing
- May have less focus on individual customization options
- Limited to 25 languages (fewer than Speaktor)
- Potentially complex implementation process for smaller organizations
- May not be optimized for personal or mobile use
Voice Dream Reader
Voice Dream Reader specializes in mobile reading experiences for dyslexic students and professionals, making it an excellent iOS narration app. It optimizes the interface for smartphones and tablets while maintaining essential functionality for on-the-go reading support, particularly focusing on educational contexts.
Pros:
- Mobile-optimized interface for smartphones and tablets
- Built-in file browser with organizational capabilities
- Strong support for EPUB and PDF formats common in education
- One-time purchase model (no recurring subscription)
- Optional premium voice add-ons for customization
- Approximately 20 language options
Cons:
- Primary focus on mobile may limit desktop functionality
- Fewer language options compared to competitors (20 vs. 50+ for Speaktor)
- Premium voices require additional purchases
- May have limited integration with learning management systems
- Could have fewer advanced customization options
- Potentially limited format support beyond EPUB and PDF
Microsoft Immersive Reader
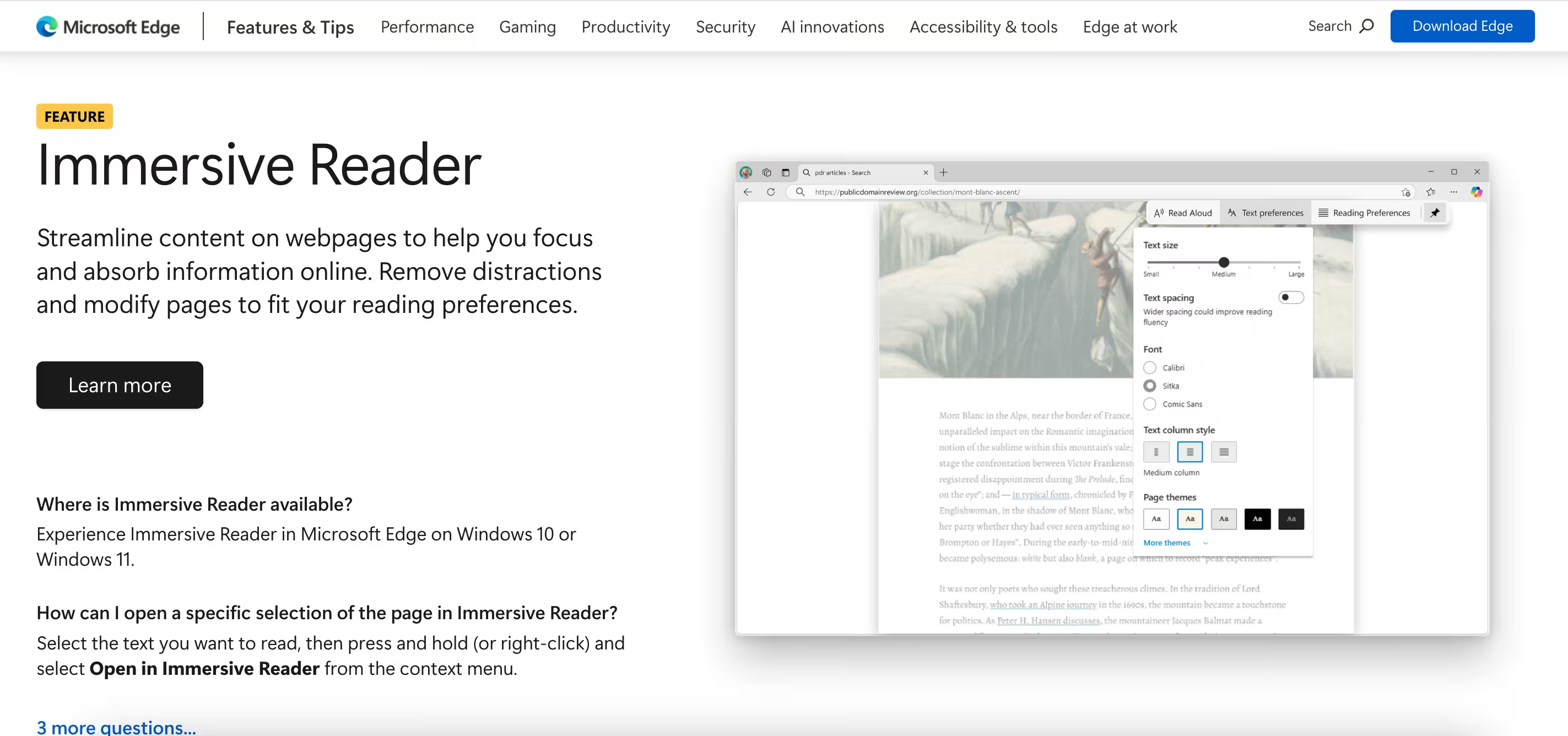
Microsoft Immersive Reader provides reading assistance directly within familiar Office applications, creating a seamless workflow for users already working in Microsoft environments. It focuses on essential support features without requiring additional software installation.
Pros:
- Direct integration with Microsoft Office applications (Word, OneNote, Teams)
- Enhanced comprehension tools like grammar and syllable highlighting
- Included with Microsoft Education subscriptions at no additional cost
- Picture dictionary functionality supporting visual learning
- No need for separate software installation
- Seamless workflow for Microsoft users
Cons:
- Limited to the Microsoft ecosystem
- Basic voice options and speed controls compared to specialized tools
- May not support external document formats as well as dedicated solutions
- Could lack advanced customization features
- No mention of language support breadth
- Potentially less natural-sounding voice quality
Speechify
Speechify focuses on simplicity and accessibility for non-technical users. It offers straightforward audio reading assistance with an intuitive interface requiring minimal setup while maintaining good voice quality for everyday reading requirements.
Pros:
- Streamlined, intuitive interface for non-technical users
- Quick setup process with minimal configuration
- Excellent mobile application experience
- Support for approximately 30 languages
- Free tier available with premium subscription options
- Ideal for casual readers and basic reading assistance
Cons:
- May lack advanced customization options of premium tools
- Premium features require a subscription (recurring cost)
- Potentially fewer document format compatibilities
- Could have less natural voice quality than premium options
- Might not have enterprise-level integration capabilities
- Possibly fewer specialized features for academic or professional contexts
How Does Text-to-Speech Technology Work for Dyslexia?
Understanding the underlying technology powering reading assistance dyslexia tools helps users select appropriate solutions and maximize potential benefits:
The Science Behind Audio Processing for Dyslexic Readers
Modern AI reading tools for dyslexia utilize sophisticated neural networks to convert written text into spoken content. Unlike robotic voices characteristic of earlier technology generations, current systems analyze contextual factors, syntactic structure, and semantic meaning to produce natural-sounding output that reduces cognitive processing demands.
For individuals with dyslexia, this advancement proves crucial since unnatural speech patterns create additional cognitive load during information processing. Advanced systems like Speaktor deliver human-like voices that minimize listening fatigue while maximizing comprehension and retention rates when using reading assistance dyslexia technology.
What Customization Options Benefit Individual Dyslexic Needs?
Each person with dyslexia experiences different specific challenges when processing written information. The most effective digital text readers for learning disabilities acknowledge this variation by offering extensive customization capabilities. Users can adjust reading speeds without pitch distortion and select from diverse voices, including different accents and tonal qualities. Text highlighting synchronization options strengthen connections between written and spoken words for improved comprehension.
Font adjustments for accompanying text, color overlay options, and contrast settings further enhance readability when using reading assistance dyslexia tools. Some solutions provide pronunciation dictionaries for specialized terminology, ensuring accurate audio reading assistance for technical content. These personalization features enable users to create optimized reading environments tailored to specific needs and preferences based on individual dyslexia characteristics.
How to use Speaktor for Reading Assistance for Dyslexia?
The step-by-step process for using Speaktor's reading assistance dyslexia features includes:
Create an Account: Register for a new account or log in to your existing account through the secure portal.
Upload documents and convert to audio with Speaktor's natural voices providing reading assistance for dyslexia. Navigate to the Dashboard: After logging into your account, the system directs you to the dashboard where the "Read Aloud" functionality appears. Select this option to begin.
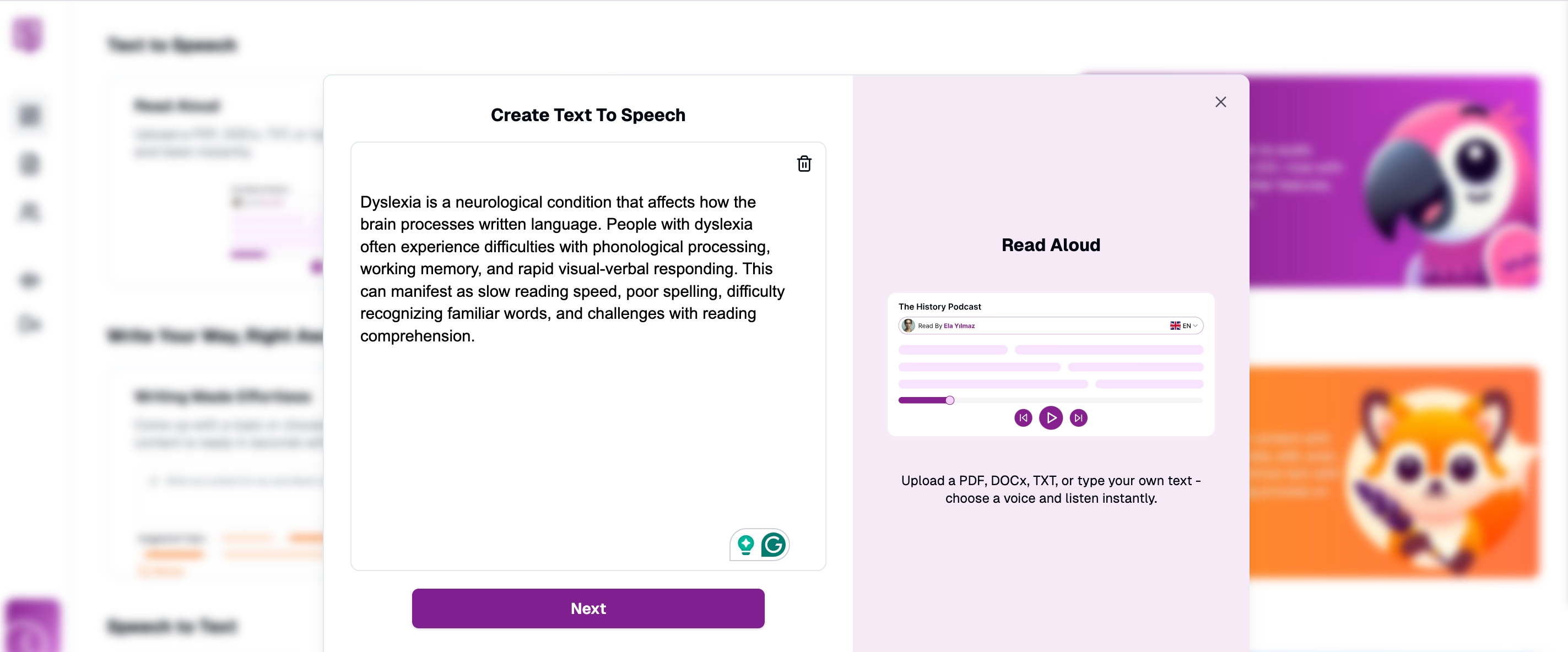
Understand reading challenges with Speaktor's text-to-speech conversion providing essential assistance for dyslexia. Input Your Text: Copy and paste written content, type manually, or select specific files requiring audio reading assistance.
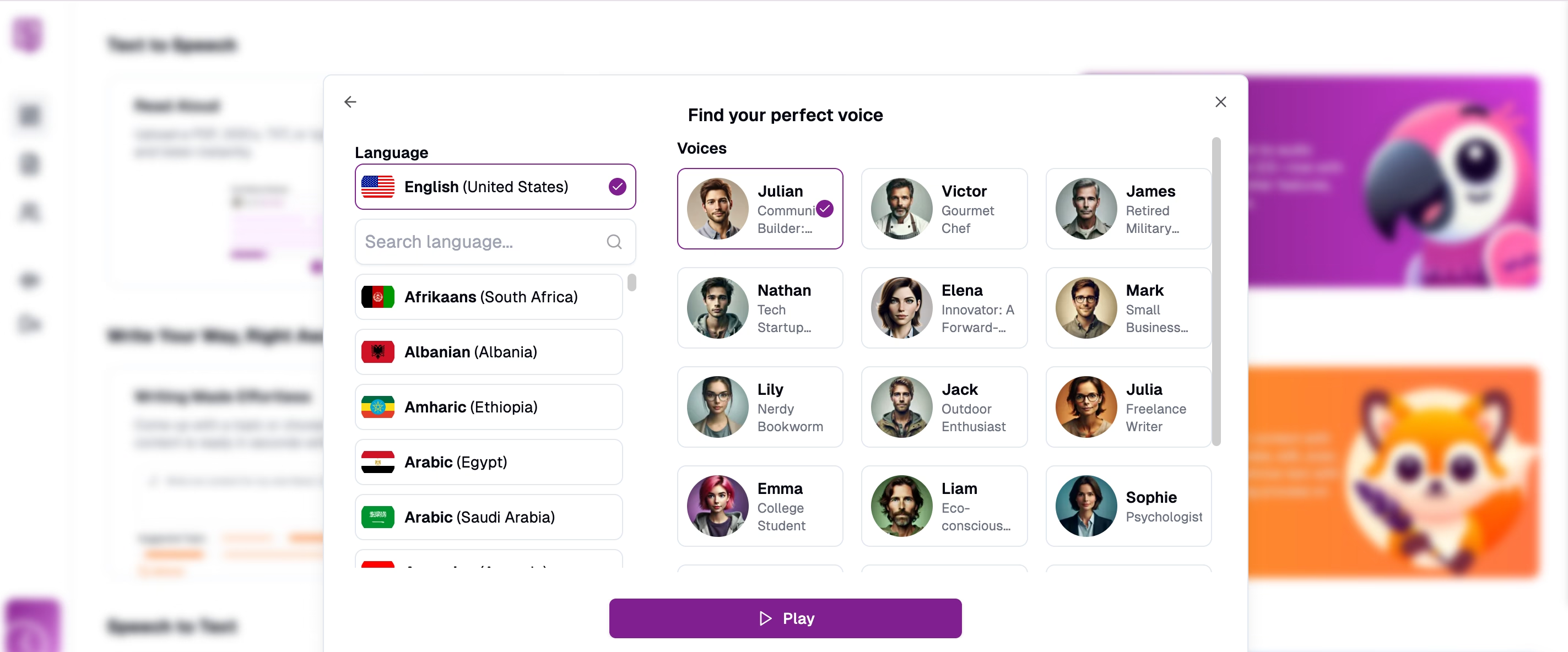
Personalize reading assistance for dyslexia by selecting from natural-sounding voices in multiple languages and accents. Select Language and Voice: Choose from more than 50 available languages ensuring appropriate selection for your content. Select from 16 different voice options offering various tones and pitch characteristics. Voice selection can be modified later if needed.
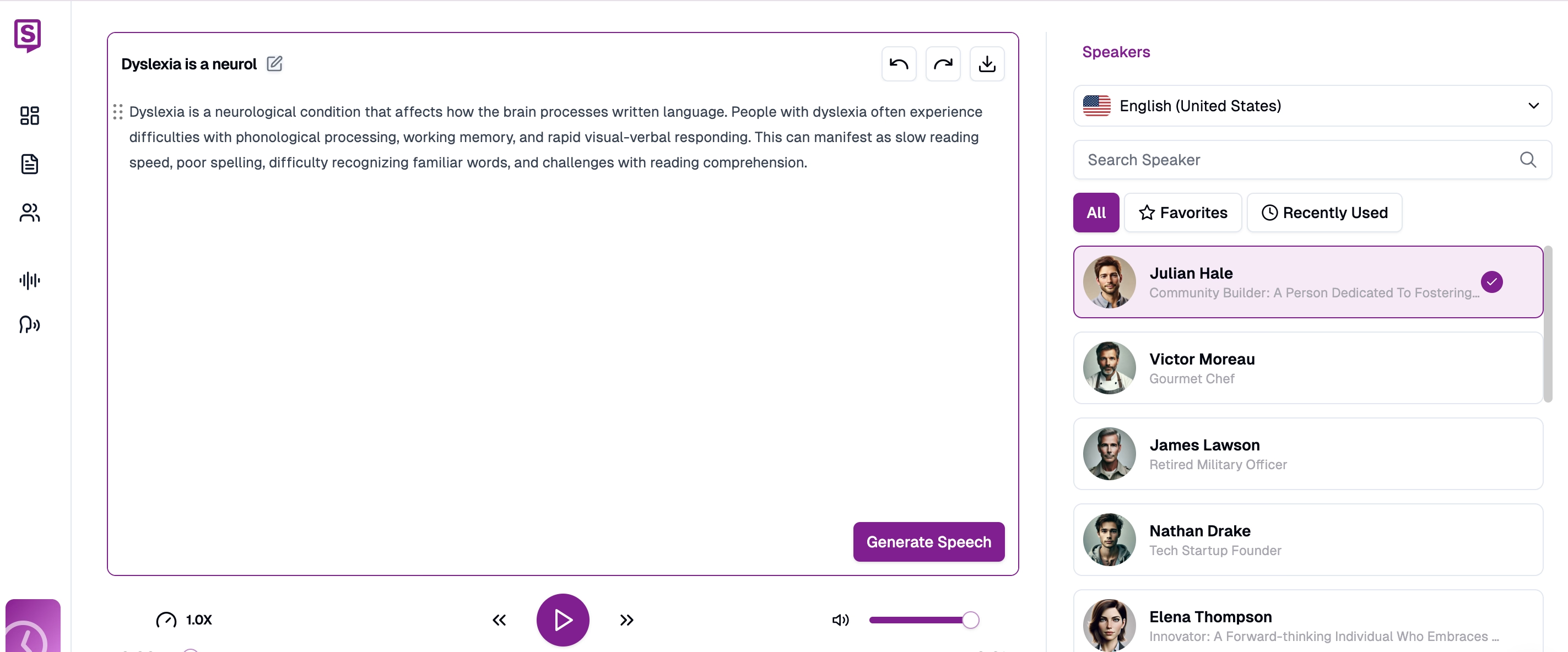
Create accessible content with Speaktor's interface that provides reading assistance for dyslexia with preferred voices. - Initiate the Reading Process: Activate the play function to begin the audio conversion. The reading assistance dyslexia tool highlights text portions during reading, enabling easy visual tracking alongside audio input.
What Strategies Maximize Reading Assistance Benefits?
To optimize results from Speaktor and similar reading support apps for dyslexia, users should establish distraction-free environments during listening sessions and consider using quality headphones for improved concentration. Many dyslexic individuals find beginning with shorter documents helpful until identify optimal listening speed settings. Combining audio input with visual text tracking provides multi-sensory learning advantages that enhance information retention rates.
Building organized libraries of frequently referenced materials streamlines workflow efficiency when using reading assistance dyslexia technology. Utilizing available tagging systems helps categorize documents by subject matter or priority level for improved resource management. Many dyslexic users report significant improvements in comprehension abilities and information retention after establishing consistent usage patterns with text-to-speech technology as part of daily routines.
Conclusion
Reading assistance dyslexia technology has evolved dramatically in recent years, offering unprecedented support for individuals with reading challenges. Today's solutions transform reading from a frustrating obstacle into an accessible, even enjoyable experience for dyslexic individuals. Among available options, Speaktor distinguishes itself through natural voice technology, extensive language support, and versatile document-handling capabilities that address diverse user needs.
By leveraging these powerful reading assistance dyslexia tools, individuals with dyslexia access information more efficiently, perform better in academic and professional environments, and experience increased confidence through greater independence. Whether supporting students, professionals, or family members with dyslexia, appropriate technology selection makes substantial differences in reading outcomes. Ready to transform reading experiences? Try Speaktor today and discover how effortless reading becomes with proper dyslexia reading software support.
Frequently Asked Questions
The best text-to-speech tool for dyslexia is Speaktor. It is designed to support individuals with reading difficulties by converting text into natural-sounding speech. Speaktor enhances comprehension, reduces reading fatigue, and helps users engage with content across formats like PDFs, Word documents, and web pages.
Speaktor reduces the cognitive effort required to decode words by reading text aloud, allowing users to concentrate on understanding content. This helps people with dyslexia stay focused longer, reduces fatigue, and supports more efficient learning.
Yes. Text-to-speech tools like Speaktor assist dyslexic adults by reading emails, reports, and complex documents aloud. This reduces reading stress, boosts productivity, and supports workplace independence.
Yes, Speaktor supports over 50 languages, making it ideal for multilingual users with dyslexia. Whether reading in English, Spanish, French, or Turkish, Speaktor ensures accessibility across diverse language needs.

